(Seoul=Yonhap Infomax) Yong Wook Kwon, GiSung Yu = Amid growing uncertainties both domestically and internationally, funds are flocking to foreign currency deposits as foreign exchange market volatility increases. While interest rates on fixed-term foreign currency deposits at commercial banks have plummeted by around 1 percentage point in the past six months, the interest rate gap between banks has also widened significantly.
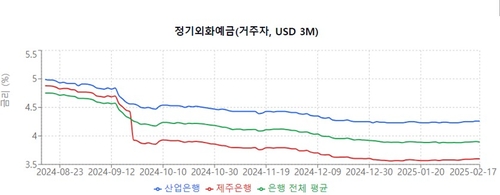
According to Yonhap Infomax on the 18th, the average interest rate for fixed-term foreign currency deposits (3-month USD) for residents at commercial banks was 3.89% as of the previous day, down 0.86 percentage points from 4.75% on August 19, about six months ago.
Resident fixed-term foreign currency deposits are financial products where domestic customers deposit major foreign currencies like the US dollar and receive interest for a specified period. They are primarily used to diversify overseas asset portfolios or as a hedging tool. While exposed to exchange rate and interest rate risks, they are utilized when seeking relatively stable returns.
The recent sharp decline in fixed-term foreign currency deposit rates indicates a surge in market liquidity. Abundant liquidity both domestically and internationally has lowered funding costs, leading banks to trend towards lowering interest rates.
In particular, as concerns over trade wars grow with the inauguration of Donald Trump's second administration in the United States, foreign exchange market volatility has increased amid external uncertainties. Until recently, domestic political risks also peaked, causing the dollar-won exchange rate to fluctuate. As the dollar-won exchange rate fluctuates, demand for more stable fund management has increased.
Moreover, over the past six months, as the US Federal Reserve (Fed) implemented monetary easing policies, US bond yields declined, which is analyzed to have been reflected in the foreign currency fund management of domestic financial institutions.
As fixed-term foreign currency deposit rates plummeted, the gap between banks also widened.
Six months ago, interest rates at commercial banks ranged from a low of 4.56% to a high of 4.99%, a difference of about 0.3 percentage points. However, as of the 17th, rates ranged from a low of 3.6% to a high of 4.26%, expanding to over 0.6 percentage points.
This widening gap is due to some banks showing particularly pronounced declines in deposit rates. Typically, when a bank's foreign currency deposit rate is significantly lower than other banks, it is interpreted as the bank choosing a conservative strategy in terms of strengthening competitiveness or risk management.
Jeju Bank led the recent interest rate decline, lowering its rate by 1.28 percentage points from 4.88% to 3.6% over six months. Conversely, Korea Development Bank reduced its rate by 0.73 percentage points during the same period, offering the highest rate among banks at 4.26% as of the previous day.
Kyongnam Bank, Gwangju Bank, KB Kookmin Bank, Industrial Bank of Korea, NH Bank, DGB Daegu Bank, Busan Bank, Suhyup Bank, Shinhan Bank, Woori Bank, Jeonbuk Bank, SC Bank Korea, and KEB Hana Bank each showed interest rates close to the average level.
An industry official commented, "Resident depositors should check the interest rate differences offered by banks, and can maximize return differences based on individual investment strategies, especially through the pronounced interest rate gaps between banks."
He added, "Financial investors and resident depositors need to closely monitor changes in external economic conditions and monetary policies and respond quickly."
ywkwon@yna.co.kr
(End)
<Copyright Holder (c) Yonhap Infomax, Unauthorized Reproduction and Redistribution Prohibited, AI Learning and Utilization Prohibited>
Copyright © Yonhap Infomax Unauthorized reproduction and redistribution prohibited.

